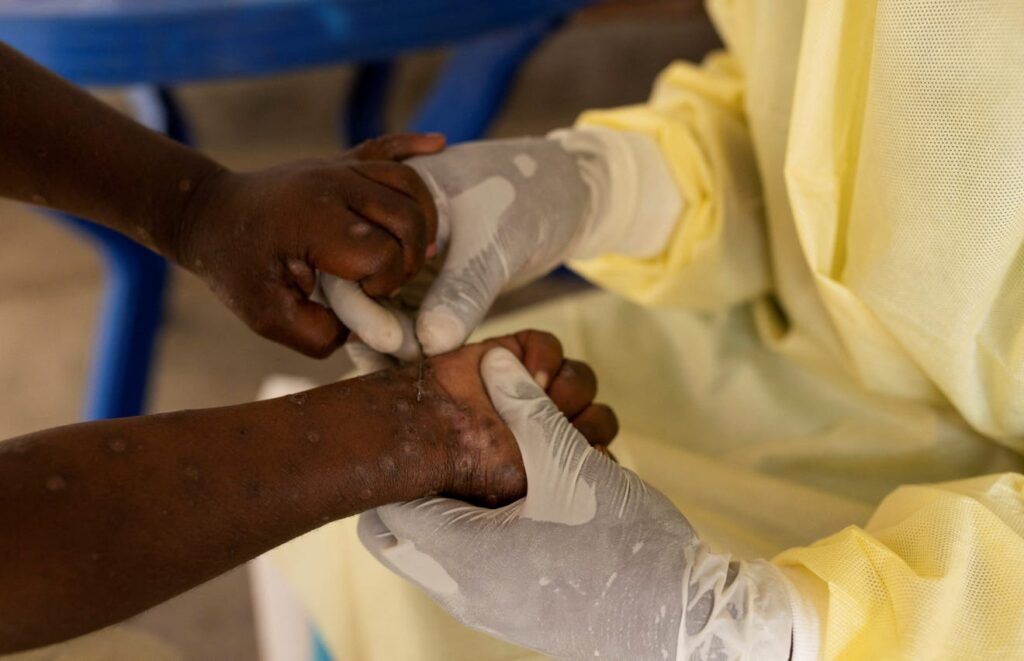
Umuahia, Nigeria – The Abia State Government has confirmed its first case of Mpox (formerly known as Monkeypox), according to the Commissioner for Information, Prince Okey Kanu.
The announcement was made during the state’s executive council meeting held on Monday.
Prince Kanu disclosed that out of 13 suspected cases, one tested positive, nine were negative, and three remain uncertified. Fortunately, no deaths have been reported.
The confirmed case is located in Isialangwa. In response, the state has opened several treatment centers, including one at the Abia State University Teaching Hospital, with plans to establish more in the near future.
Dr. Ngozi Azodo, the Special Adviser on Health, emphasized the collaboration between the Ministries of Health, Environment, and Public Utilities. She also mentioned that a steering committee has been established to address infectious diseases, aligning with the Federal Government’s “One-Health” policy. The state government is committed to enhancing surveillance and strengthening healthcare facilities to better respond to such health threats.
In her statement, Dr. Azodo urged citizens to maintain good hygiene, minimize contact with animals, and avoid close contact with individuals suspected of having the disease.
Additionally, Dr. Azodo announced that the state Ministry of Health is set to renovate and retrofit 200 Primary Healthcare Centres (PHCs) across Abia within 100 days.
This ambitious project is scheduled to begin in the first week of September, with completion targeted for December as a “Christmas gift” to the people of Abia.
what you should know about mpox
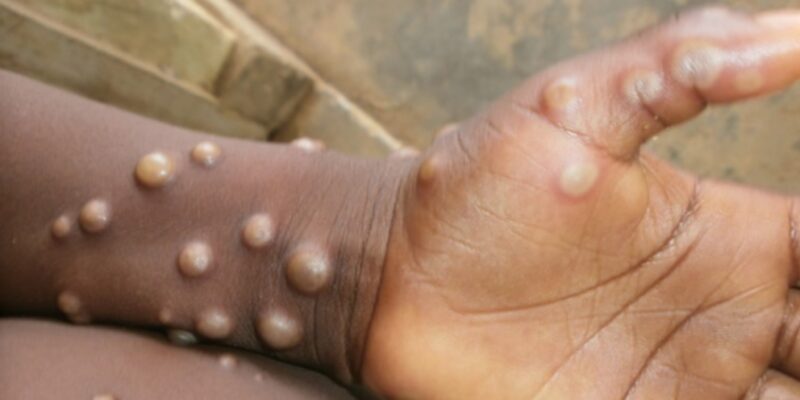
Mpox, formerly known as monkeypox, belongs to the same viral family as smallpox, but is unrelated to chickenpox, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Initially identified in 1958 in monkeys, the virus was named monkeypox, but has since been renamed mpox to reduce stigma.
As a zoonotic disease, mpox can transmit from animals to humans and also spread between people through physical contact. Notably, human-to-human transmissions have increased since 2016.
There are two main types of mpox: clade I, found in central Africa, and clade II, found in West Africa. A new variant, Ib, has emerged from clade I and appears to be more contagious.








Join our Channel...